
How the Oil Filter Works
As a rule, in modern cars the oil filter is mounted on the oil pump housing. The thread on the central opening of the filter corresponds to the thread of the rod on which it welds to the tight fit of the sealant to the pump housing. An engine driven oil pump absorbs engine oil through a special oil receptacle with a grid (to prevent large contaminations) from the engine tray and pumps it to all places that require lubrication. Uncleaned oil comes through small openings, passes through a filter system, made of special paper or synthetic material, and comes out purified through a central hole in the engine.
The oil filter consists of two media types: primary and secondary. Primary types designed to stop large particles that are bigger than 20 microns (0.02 mm). The secondary ones are filtered and captured by smaller pollutants in the size of 5 microns (0.005 mm).
In a good quality filter, the movement of the oil is not disturbed: to prevent the outflow of oil during the parking of the car a reverse valve is provided. It is a special filter paper that is installed in a metal clip, which prevents the wrinkle (and often reinforced by a metal grid on the outside), and the joints are securely sealed.
Cases and covers are made of durable steel with anti-corrosion coating, and rubber elements are not affected by the influence of oil and high temperatures.
Bypass valve is an engine protection from oil shortage. When the engine oil becomes thicker (after a winter stand), or when the filter is very dirty and does not allow sufficient oil to flow, a bypass valve opens under pressure, through which the oil passes bypassing the filter element. Thus, the engine will not suffer (at once; the oil and filter will still have to be changed).
The longer the filter is installed in the car, the more pollution it contains. When the oil passes through such a filter, the cleaning procedure will not take place.
Oil filters can have a different design: a removable, so-called "spin-on", or as a cartridge-insert, an "oil cartridge". Removable filters such as "spin-on" are exchanged for the new ones after the term of use is due, while in the "oil cartridge" only the cartridge of the oil filter element, which is installed in the case, has to be changed.
Types of oil systems according to the scheme of filters inclusion:
1. Full-flow oil systems
2. Part-flow oil systems
3. Full/part-flow (combined) oil systems
Full-flow is the most common type of filter, which is installed on most cars. The oil from the pump enters the filter, passes through the filter element and after being cleaned is moving further down to the units of the engine. In such system, all circulating oil passes through the filter, and the bypass valve acts as a fuse against a critical increase in pressure.
The partial flow filter has a much lower rate of filtration, which is not enough for the entire oil to pass through the filter element. In this case, the filter is installed in parallel to the oil line and the refined oil is merged into the engine crankcase. The quality of cleaning is a bit higher than that of a full flow filter.
Combined filters have in their design both full-flow and partial flow elements (as in the modular system) or filters of two different types and are installed in parallel.
Full-flow oil systems
All engine oil, which is absorbed by an oil pump, passes through the oil filter before it comes to places that require lubrication.
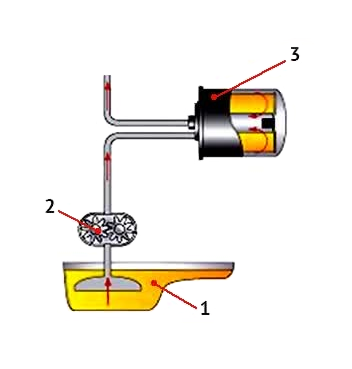 Since the oil pump is directly connected to the engine, and the oil pressure depends on the rotational speed of the engine shaft, a safety valve, which is an integral part of the design of the oil pump, is provided for limiting the maximum pressure. Typically, this safety valve limits the pressure in the oil system between 3 and 5 kg / cm2.
Since the oil pump is directly connected to the engine, and the oil pressure depends on the rotational speed of the engine shaft, a safety valve, which is an integral part of the design of the oil pump, is provided for limiting the maximum pressure. Typically, this safety valve limits the pressure in the oil system between 3 and 5 kg / cm2.
When the oil pressure exceeds this limit, there is a risk that the gaskets and the centering disc may be damaged or extruded from their seats. Sometimes, when the oil pressure rises too high and the safety valve of the oil pump does not open two things can happen. The the oil filter gasket is being extruded from its place and the oil starts to come out from the filter or the oil filter housing is inflated.
Usually, the oil filter is being undeservedly blamed in this case, although the fault is on a safety valve for the oil pump. And after the engine and the oil pump cool down (restored), the safety valve usually starts working again, eliminating the evidence of the real cause of the problem.
To prevent a large difference in pressure between the dirty and clean sides of the filter element, the design of the filter has a bypass valve. This valve opens at a pressure drop of 1-2 kg / cm2, and thus the engine oil (even uncleaned) can still lubricate the engine parts, even with a completely clogged dirt filtering element.
In addition, there is an anti-drain valve that prevents the oil from filtering back into the crankcase when the engine is turned off. Some filter designs have an anti siphon tube, which also prevents oil from filtering off after turning off the engine.
The pressure drop across the filter and its resource (filter capacity) must meet the requirements of a vehicle manufacturer. Therefore, when selecting a replacement filter, it is necessary to carefully consider many specific parameters, and not only the connecting and overall dimensions. Sometimes a similar but cheaper oil filter can vary greatly in the filtering parameters of a high-quality filter, properly designed for a particular car.
Part-flow oil systems
The engine oil is being absorbed by the pump from the engine crankcase and is served directly to the lubrication points under pressure. But in addition to the main oil mainline, there is a parallel line, in which a partial flow filter is installed. Approximately 10% of the oil from the main stream is passed through a parallel line with an oil filter and, therefore, is filtered. The ratio of oil that flows in the main and parallel lines is determined by the calibration openings located in the oil filter.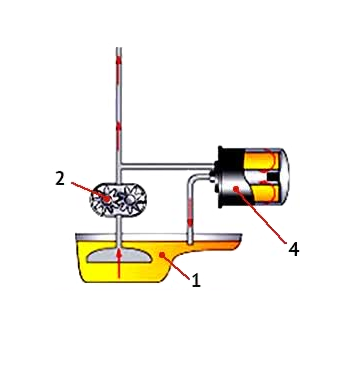
Although the main oil flow enters the engine without cleaning while bypassing the oil filter, in general, the efficiency of the partial flow circuit is very high.
Unlike the air filters that operate on the principle of "one-pass cleaning", oil filters use the principle of "multi-pass cleaning" (the same engine oil is repeatedly passed through the same oil filter). Therefore, if polluting particles can first bypass the filter in the main stream, they will be detained by an oil filter while traversing a parallel line.
Moreover,, for a partial flow scheme, more time will be required to filter out all polluting particles. However, when comparing efficiency, the partial flow system provides the same level of engine protection as full flow.
Combined oil systems
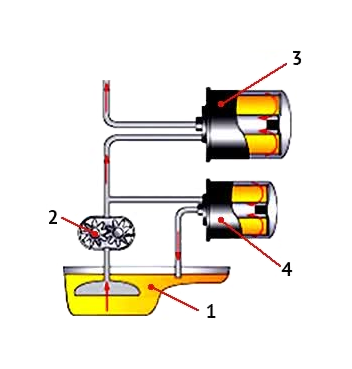 A combination of full-flow and partial-flow systems is commonly used for heavy machinery (diesel engines for trucks, industrial and earth-moving machinery). Approximately 90% of engine oil is filtered through a full-flow filter, and 10% of the oil is circulated in the engine crankcase through a partial flow filter.
A combination of full-flow and partial-flow systems is commonly used for heavy machinery (diesel engines for trucks, industrial and earth-moving machinery). Approximately 90% of engine oil is filtered through a full-flow filter, and 10% of the oil is circulated in the engine crankcase through a partial flow filter.
The result of this filter combination is the creation of very good conditions for the engine oil use and, as a result, a significant increase in oil and filter lifetime.
Filtration subtlety
There are 2 parameters to assess the subtlety of filtration - the nominal subtlety of the filtration and the absolute one. The nominal subtlety of the filtration is the size of the particles that are retained by the filter by 95%, the absolute subtlety of the filtration is the size of the particles that are completely retained by the filter. In domestic practice it is accepted to evaluate filters by the nominal subtlety of filtration. For example, in road-building machinery, the nominal subtlety of filtration of most hydraulic system filters is 25-40 microns (0.025-0.04 mm). In aviation, filtration requirements are tougher, and the nominal subtlety of filtration of most filters is 5 microns (0.005 mm) or less.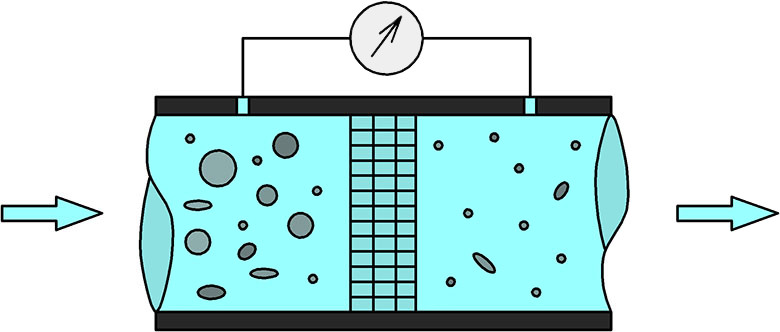
The finer the filtration, the greater is the fluid flow of the filter resistance, but, on the other hand, the lower is the effect of contamination in the working fluid on the wear of parts of the hydraulic equipment.
Modern diesel and petrol engines are sensitive to pollution, even minor solid inclusions can disrupt the perfectly balanced system. But along with excellent performance, safety and power, these engines require high-quality filters.
The filtration subtlety of the oil filter is an indicator of the largest particle size that can pass through the filter. For example, coarse filters have an index of thinness of withdrawal of 45 microns (0.045 mm), which means that all particles greater than 45 microns are detained by this filter. For the car, a filtration of not more than 5 microns is required, so all the partial flow filters have an index of thinness of withdrawal of no more than 5 microns (typically 3-4 microns (0.003-0.004 mm)).
It is possible to achieve the desired filtration subtlety by using high-quality materials, as well as other methods for cleaning motor oil (as in centrifuge centrifuge filters, for example). But the full filtering takes place quite slowly (the filter has a low bandwidth), so the combined systems give a better effect than one filter.
Based on online resources
Leave a Reply Cancel Reply
All fields are required